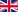
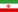
What is a Roof Garden?
Nature on a building!
As our cities keep growing larger and our personal living spaces gradually shrink, more and more people are turning to roof gardens as a way to utilize wasted spaces and bring peace and nature back into their living environments. Any building has a roof and so it can also have a roof garden. The idea of constructing a roof garden seems like an obvious choice.
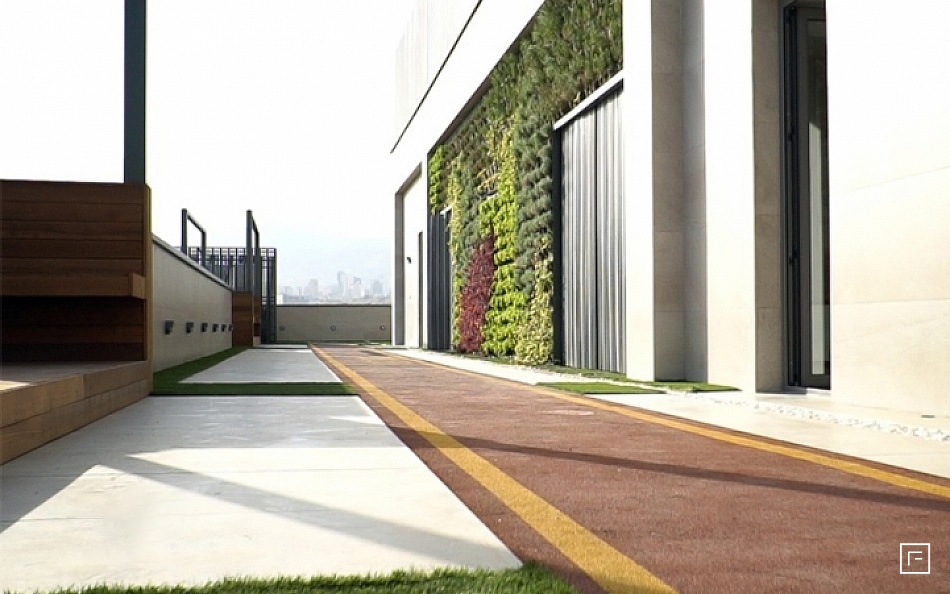
Roof gardens offer a pleasant atmosphere on villas, apartments, houses and industrial or commercial buildings and has become a relaxing environment for its residents.
Other usages of the roof garden include a space for recreation and sports, children's play, a suitable place to have a private meeting, creating shade in the hot of the summer and the possibility of sunbathing on the roof or providing a suitable place for meditation and relaxation away from the hustle and bustle of the city.
Roof Gardens have significant effect on creating a positive mood for family members and helps you to be safe and away from the city's crowds, pollution and a stressful day even for an hour.
Creating an ornamental and decorative environment, a roof garden improves the level of architecture in a building and, in addition, increases the beauty of the buildings and the entire city as well.
If you want to have a roof garden and need guidance, you can contact Fartak Group experts. Contact Us
FARTAK GREEN ARCHITECTURE
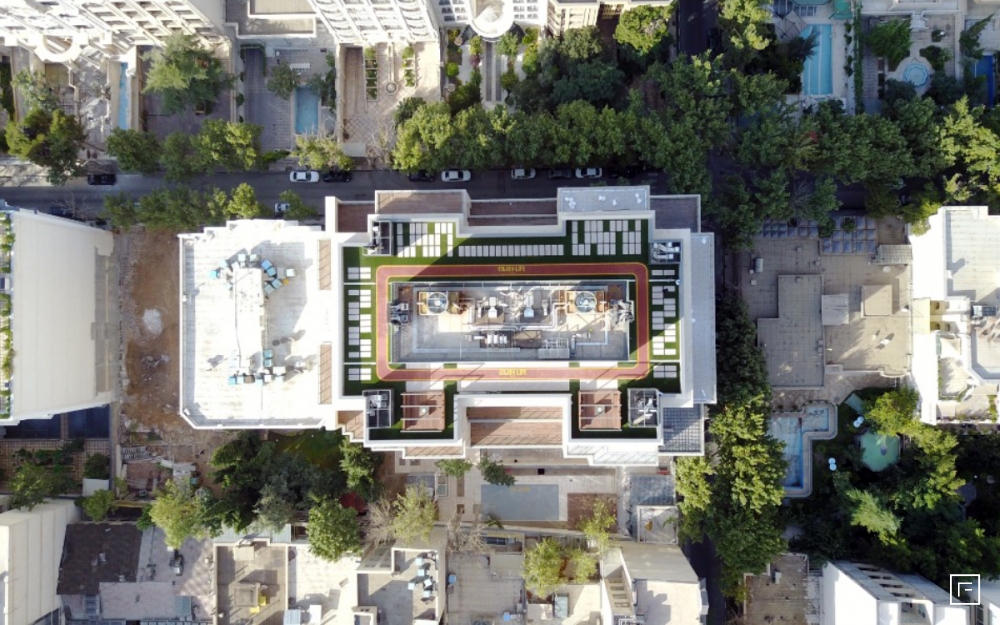
BARAN TOWER
MASHHAD-IRAN
Roof Garden Design and Construction
Important Points in designing and building a roof garden:
1. Checking the strength and weight of the roof
The roof must be able to support the additional weight of building materials, plants and growing bed (250 kg per square meter), so your roof may have to be modified or reinforced to provide resistance. Choosing between a wide and lightweight roof garden or a compact roof garden is determined based on the additional weight and strength of your roof. A wide roof garden is lightweight and designed to support a shallow layer of vegetation and soil (more than 20 cm). A compact roof garden, on the other hand, is used with structural support to accommodate deeper soil, a greater variety of plants, an irrigation system, and even some of the amenities found in a typical backyard, such as a barbecue.
2. Checking the shadow
The roof garden is exposed to full sunlight for most of the day time, so it shall be closely considered that where to provide shade for shade-loving plants as well as for people.
3. Wind
The roof can be exposed to strong wind in adverse weather conditions of an area. Therefore, it is tried to fully consider the wind in the design plan.
4. Privacy
If you live in a residential area, you may be exposed to your neighbors and could be seen easily, so we need to consider ways to create privacy. In this instance, strategically placed trees or sunshades are preferred over building panels or fences.
5. Access
Examining the solution for transferring workers and construction materials
6. Irrigation
Equipping and designing a smart irrigation system for regular irrigation of green spots
FARTAK GREEN ARCHITECTURE
PANAMERA-MIKA
TEHRAN-IRAN
7. Planting Design
Selection and arrangement of seasonal and non-seasonal resistant evergreen plants... suitable for environmental conditions - planting bed - climatic conditions, as well as providing visual beauty of the desired space.
8. Planting bed
Here is a brief reference to the structure of roof garden planting bed:
1. Waterproofing Layer
The desired surface for creating a roof garden should be waterproof and sustainable and have the necessary resistance for creating and expanding the green space in the desired planting bed. In fact, creating a waterproof layer is the most important layer in the structure of a roof garden so that it covers all the holes and openings in the planting bed.
2. Insulation Layer
The isolation or protector layer actually provides the planting bed with resistance against moisture and temperature changes, as well as the required mechanical strength. This layer is usually made of XPS polystyrene sheets, PIR panels, or polyurethane foam.
3. Drainage Layer
The drainage layer in the roof garden is a very important layer in the roof garden infrastructure, which manages the rainwater on the roof garden. In fact, in addition to draining and quickly transferring water during rain, this layer keeps the water needed by the plant available and reduces the volume of spilled water by absorbing the water.
4. Geotextile Layer
Geotextile is actually a layer that works as a divider that separates the drainage layer and the soil where the plant grows. It also prevents the accumulation and retention of soil as well as particles that may cause the drainage layer to close. Furthermore, through circulating humidity, it will neutralize the effect of rapid decrease in the amount of water. Geotextile must have water vapor permeability and also be strong and resistant in terms of chemical and mechanical structure.
5. The Vegetation Layer
The outer layer or the soil in which plants and greenery can grow. In this space, water permeability and air circulation are important factors for average plant growth. The type and thickness of the soil used depends on the type of the plant that is planted on the growth layer.
Usually, the plant needs fertile and acidic soil to grow, which is a combination of compost garden soil and organic elements.
Here are some advantages and disadvantages of building a roof garden:
Why having a Roof Garden? Building a roof garden within a green architecture would elevate the level of the topics relating architecture. In addition to creating extraordinary visual beauty and a pleasant atmosphere, nature on a building has a great impact on urban beautification through:
- Oxygen production - reducing the emission of carbon dioxide in the air and allowing you to breathe clean fresh air
- Decrease in the temperature of a building - reducing the amount of energy consumption and also the temperature of the surrounding spaces
- Creating a habitat for some animals and maintaining the ecological cycle
- Rainwater storing, management, and control
- Creating a suitable and usable space, it will increase the value of a building and ultimately increase the price value of that building at the time of sale and lease
- Increasing the lifespan of the roof by covering the top surface and through lower layers of the roof garden
- In several countries, such as the United States of America, the government refuses to collect property tax from the owners of buildings with roof gardens
- Providing protection against sudden changes in the temperature
- The results gained from construction of a roof garden create a balance in urban climate changes
- Positive impact on social relations and decreasing air pollution could also be another benefit of building a roof garden
And some disadvantages of a roof garden:
If the principles and methods for building a roof garden are not correctly observed and followed, the structure and weight of the roof may cause challenges for the entire building.
Increasing the amount and cost of water consumption
Unlike traditional gardens, the construction of a roof garden requires a complex and costly drainage system which does not allow for any cracks or holes leading to the interior of the building. If the cleansing and preparation of the desired space is not done prior to the construction operation, there is a possibility of creating living conditions suitable for some species of reptiles. Moreover, if necessary substances for prevention and control of the pests and diseases of the plants are not injected to the cultivation soil beforehand, then there might provide a space to attract disease-carrying insects.
Download Roof Garden Catalogue